Nowadays, mobile internet is not limited to mobile phones only but can easily be extended to other devices through tethering and hotspots. With 4G LTE and 5G NR mobile phones, tethering and mobile hotspotting techniques are handy alternatives if your main internet goes down.
4G and 5G smartphones today have the option to enable a mobile hotspot on your phone to allow you to share the 4G LTE or 5G mobile internet with other Wi-Fi enabled devices such as laptops, smart TVs and tablets. Tethering is not limited to Wi-Fi and can also be achieved via USB cables or Bluetooth.
What is the difference between tethering and mobile hotspots?
Tethering and mobile hotspots in 4G and 5G phones are interrelated as hotspots are a type of tethering. A mobile hotspot uses a WiFi connection to tether to the devices that need the internet, e.g. a laptop. Tethering is not limited to WiFi and can also be achieved through USB cables and Bluetooth.
Tethering and hotspots are interrelated terminologies; however, tethering is a broader term as it represents a connection that can be wired or wireless. For example, tethering can occur when you connect your mobile phone to a laptop via a USB cable, Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. On the other hand, a mobile hotspot usually refers to using your mobile phone as a Wi-Fi hotspot. However, the term hotspot or personal hotspot covers Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and USB tethering on certain mobile devices such as iPhones.
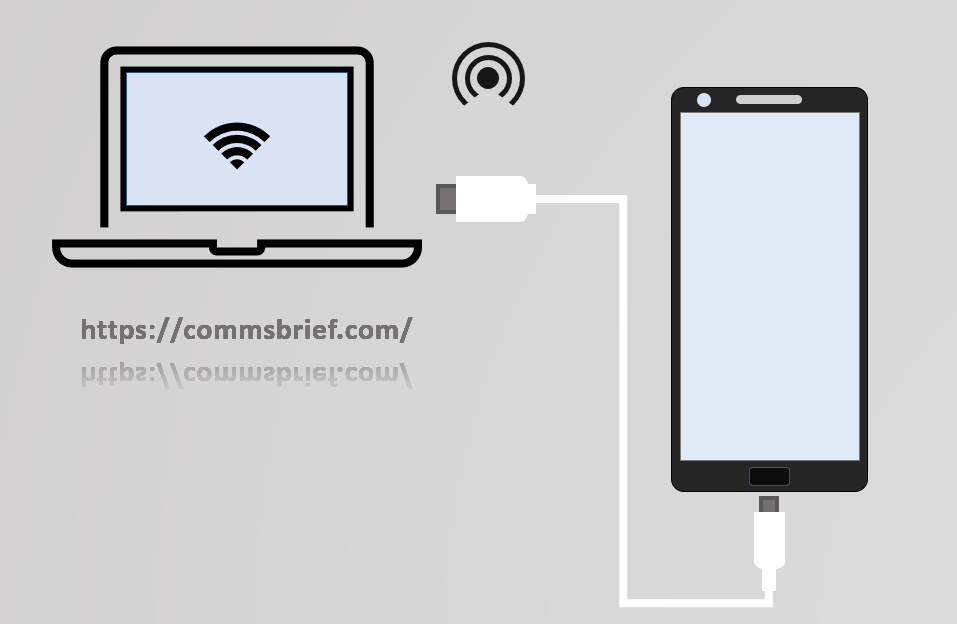
Tethering in mobile communications refers to a technique that allows your mobile phone to share its mobile data (cellular data) with other internet-enabled devices. The most common way of achieving that is by enabling the mobile hotspot option on your phone. The other handy option is using a USB cable, especially if you need to connect only one device to the internet, e.g. your work laptop. The picture below depicts the high-level concept of tethering and hotspots. Even before the 4G networks, we used devices like 3G data cards and USB dongles to connect our laptops to the internet. Those devices used high-speed packet access techniques like HSPA and EVDO to enable the internet through cellular networks. With the evolution of 4G LTE, the average data speed achievable through mobile networks has improved considerably. As a result, mobile hotspots or tethering have increasingly gained popularity over the last few years.
Tethering means connecting your phone to other devices to share internet
When you connect your mobile phone to any other device through a wired or wireless connection, that means you are using the tethering capability on your phone. When tethered to another device, your mobile phone allows you to share the mobile internet with that device. In today’s world, with the advent of 4G and 5G network technologies, tethering can allow you to share your phone’s high-speed mobile internet with other internet-enabled devices such as laptops, tablets, smart TVs, and set-top boxes (STB) and many other devices.
Mobile hotspot means creating Wi-Fi coverage through your phone’s internet
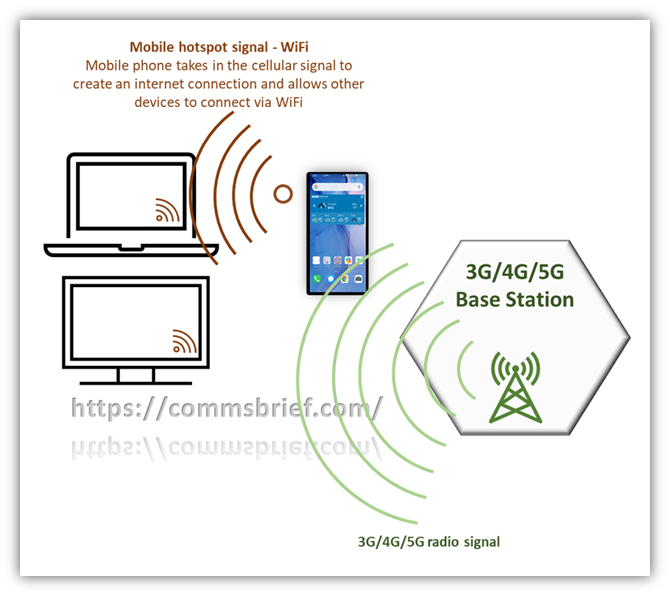
A mobile hotspot is when you use a mobile cellular device such as a smartphone or a SIM-enabled tablet to create Wi-Fi coverage that allows any internet-capable devices to connect to the internet. It was possible to do the same thing using a USB cable or Bluetooth in the earlier days, and the concept was called tethering. However, with the introduction of mobile hotspots, tethering has gone to another level because the connectivity is through WiFi instead of a cable or Bluetooth. The basic concept of hot-spotting is visualised in the diagram below.
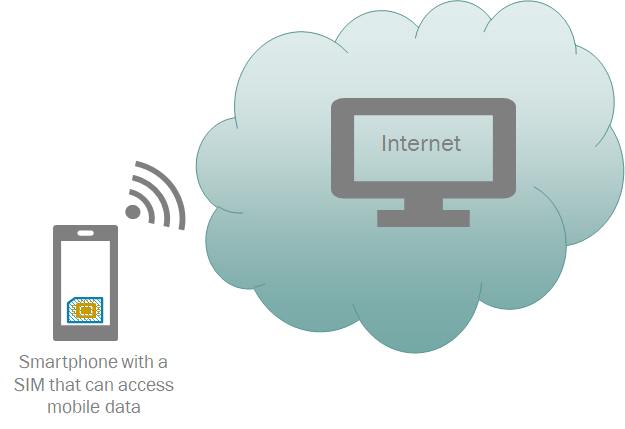
Is a mobile hotspot faster than tethering?
Tethering and hotspot do the same thing as they both allow a mobile phone to create internet connectivity for another device such as a laptop. The speed of the connection is not about tethering vs hotspot but primarily about the cellular technology being used, i.e. 3G, 4G or 5G.
If you find yourself in an area with good 4G/4G+ coverage both indoors and outdoors, you can expect your achievable data speeds to be 16-66 Mbps in download, as shown below. However, if you live in an area where you mostly only see the H+ sign on your mobile phone, you can expect lower speeds. The worst case is if you mostly have 2G coverage in your area, which can only deliver meagre data rates. We have some real-life examples below from 2G, 3G and 4G networks to show you what speeds mobile hotspots (WiFi enabled) can deliver on each of these networks.


The other thing that can also impact your speed is the type of connectivity, i.e., Wi-Fi or USB or Bluetooth. Bluetooth has a low bandwidth, and therefore, it cannot support high-speed data services. On the other hand, Wi-Fi and USB do not have this challenge and therefore are more suitable for using broadband services when using tethering. We did a quick test to compare how the download and upload speeds differ when using USB, mobile hotspot (WiFi hotspot) and Bluetooth for tethering. To do this test in a fair manner, we used the same cellular technology (4G LTE) and the same 4G phone for each test case.
| Connectivity Type | Network Type | Download Speed | Upload Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| USB cable | 4G network | 63.55 Mbps | 34.75 Mbps |
| Wi-Fi hotspot | 4G network | 50.01 Mbps | 12.59 Mbps |
| Bluetooth | 4G network | 1.31 Mbps | 1.38 Mbps |
—Tethering an Android mobile phone on 4G network to a laptop, UK, Sept 2021—
Can tethering and mobile hotspots be bad for your phone?
Tethering and mobile hotspots can quickly consume the phone battery because they require the phone to first connect to a cell tower to access the mobile internet and then create a Wi-Fi coverage zone to share the internet with other devices. Tethering and hotspot can also incur additional data charges.
When you use your 4G or 5G mobile phone as a hotspot, your nearby devices can easily connect to the internet and get decent speeds, as shown above. But to achieve that, the mobile phone has to do a lot of work which consumes extra battery power. Firstly, it consumes more data on behalf of other devices, which in turn consumes more power. Secondly, the mobile phone ends up doing a dual job, i.e. communicating with the mobile base station via 3G/4G/5G and communicating with other connected devices through WiFi, increasing power consumption considerably. The same concept applies if you are using Bluetooth tethering however, with USB tethering, you may find that you can charge your phone through your computer, so the battery drainage is potentially less. However, the main limitation of USB tethering is the fact that you can only connect it to one device at a time. On the additional data consumption side, unless you have sufficient data allowance as part of your monthly mobile plan (tariff), you may not be left with a lot of data for general phone use for the rest of the month. Therefore, from a device perspective, you are better off using a purpose-built mobile WiFi router, e.g. an LTE router or a 5G router connected to a power source to provide consistent WiFi connectivity.
Is a 5G mobile hotspot better and faster than a 4G hotspot?
As a general rule, a 5G mobile hotspot is faster and better than a 4G hotspot because a 5G hotspot can deliver higher average download and upload speeds compared to a 4G LTE hotspot. 5G can offer average download speeds of around 150 Mbps compared to 4G LTE, which can enable between 50 to 80 Mbps.
The speeds of the 5G mobile hotspot and 4G hotspot depend on which network technology is providing the service. 5G mobile networks are powered by the New Radio (NR) technology, superior to the 4G LTE technology. As a result, 5G networks can enable higher average download and upload speeds than 4G LTE. 5G networks can enable average download speeds of around 150 Mbps and average upload speeds of around 30 Mbps. The 4G LTE Advanced and Advanced Pro networks can enable average download speeds of between 50 to 80 Mbps which is lower than the average 5G speeds.
Is there an extra cost to use mobile hotspots and tethering?
If your mobile operator does not have any restrictions on tethering, then all the data consumption that results from tethering and hotspotting is deducted from your mobile data allowance. You may be charged for data overage if you go over your maximum monthly data allowance.
When you use your mobile phone as a hotspot, all the data consumption goes out of your data allowance provided by your mobile subscription. So, for example, if you have a mobile tariff that gives you 50 GB of data monthly, then whatever internet is consumed through hotspotting/tethering shall come out of that. If you don’t have a lot of data allowance in your mobile plan (e.g. 3 GB per month) and you use up all the allowance and even go over, your mobile operator may charge you for data overage. You can overcome this issue by adding data-cap or spend-cap to your mobile plan.
Mobile operators typically have policies around tethering, and in the past, there used to be some limitations in terms of how much data could be consumed when tethering. Nowadays, though, tethering has become a common practice, and most mobile operators allow tethering. In the UK, for example, mobile operators allow you to use your mobile tariff for tethering /hotspotting also because it is your data, so you can do whatever you want with it. However, depending on your country and operator, it is always best to check directly with your cellular service provider to avoid potential bill shocks. When you tether, your data consumption comes out of your monthly data allowance, which is part of your mobile plan. With many mobile operators already offering unlimited data packages, the tethering option can become even more popular.
How mobile hotspots and tethering work on 4G and 5G phones
Creating a mobile hotspot is the simplest way to tether, and it is the method most of us can easily use. Smartphones nowadays have the option to turn on the mobile hotspot to enable wireless internet connectivity. Generally, you need to go into network/internet settings on any smartphone to find this option, and when it is enabled, the phone shows a symbol like the one in the picture below.

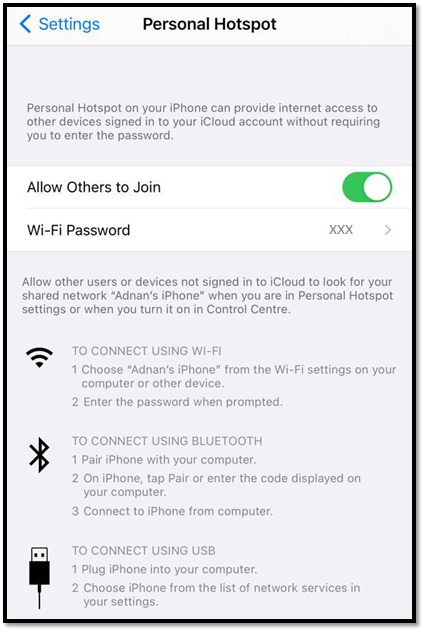
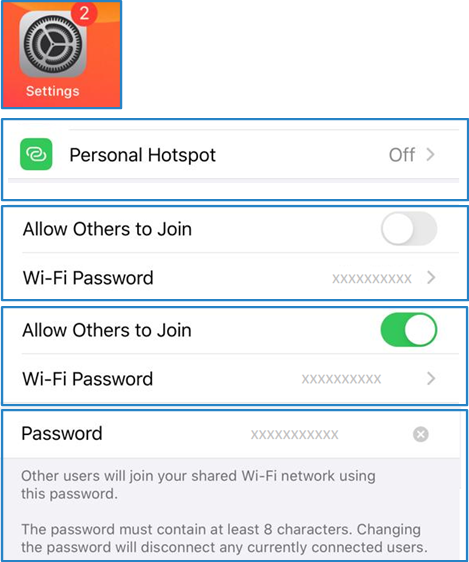
On an iPhone, you can find this option by going into “Settings” and then “Personal Hotspot”, which will display the following screen. Depending on the phone manufacturer, this option may appear in different locations on Android phones.
Smartphones make it very easy to create hotspots by tethering your phone to devices like laptops, tablets, Smart TVs and even other mobile phones. Usually, the tethering option can be found under ‘Settings’ both in the iPhones as well as the Android phones. You are likely to see the term ‘hotspot’ used in some way, e.g. personal hotspot, portable hotspot or mobile hotspot in most phones for the purposes of tethering. We have captured some examples below using an iPhone 8 (iOS) and two Android phones (Huawei Mate 10 Pro and Samsung Galaxy A10) for your reference.
How to use iPhone as a mobile hotspot?
If you have an iPhone (e.g. iPhone 8), you can follow the simple steps below. There are also some screenshots to help you visualise.
- Go to ‘Settings’
- ‘Personal Hotspot’
- Slide ‘Allow Others to Join’ to the On position
- You can click on the password and change it if you wish
How to use a Huawei Android phone as a mobile hotspot?
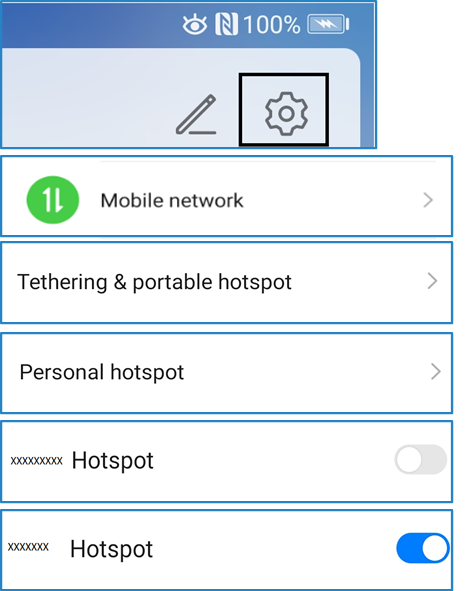
On Huawei Mate 10 Pro, which is an Android phone, you can use the following steps to create a mobile hotspot. We also have some screenshots to help you visualise.
- Go to Settings (gear icon)
- ‘Mobile network’
- ‘Tethering & portable hotspot’
- ‘Personal hotspot’
- Then you’ll see a screen with your personal hotspot name
- Simply slide the hotspot switch to the ‘On’ position and you are good to go. You may also use the options to configure your hotspot e.g. change hotspot name, password etc.
How to use a Samsung Android phone as a mobile hotspot?
If you have a Samsung Galaxy A10, you can use the following steps to create your personal hotspot.
- Go to Settings (gear icon)
- ‘Connections’
- ‘Mobile Hotspot and Tethering’
- Then slide ‘Mobile Hotspot’ to the ‘On’ position

How USB and Bluetooth tethering options work
There are at least three ways of using tethering on your phone, including two wireless options and one wired option. The two wireless options are Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, and the wired option is the USB cable. Both Android phones and iPhones support these three options; however, the terminologies are expressed slightly differently depending on the phone manufacturer. For example, in iPhones, all three tethering options are grouped under “Personal Hotspot”. In Android phones, depending on the manufacturer, the hotspot option is shown as Wi-Fi Hotspot, whereas the other two options are termed Bluetooth tethering and USB tethering.
How to use a USB cable to tether?
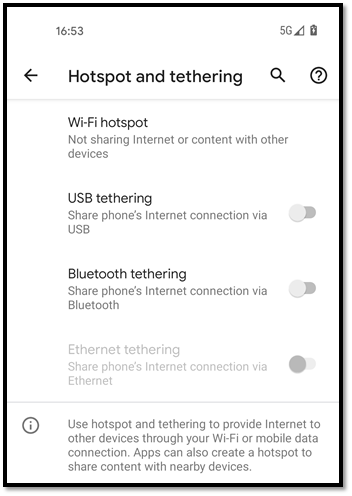
While it may be a bit uncommon nowadays to find non-WiFi ways of accessing the internet, your mobile phone can provide you with multiple ways to share your mobile internet with other devices. One handy way is the USB cable which allows you to tether your phone to your laptop whilst also charging your phone simultaneously. Below is how you tether a Google Pixel 5 phone to your laptop to access the high-speed mobile internet.
- The first and the most obvious step is to connect your mobile phone to your laptop using a USB cable.
- You then need to go into your phone settings and tap the “Network and Internet” option.
- There you can tap “Hotspot and tethering”.
- You can use the “USB tethering” toggle button to enable the sharing of the internet.
- As soon as you have done that, you should get connected and see the LAN/Internet symbol in the notification area as shown in one of the pictures below.


How to use Bluetooth to tether?
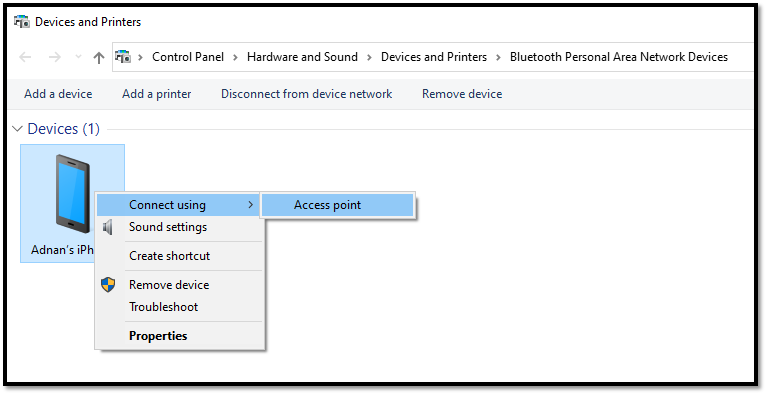
If you want to use Bluetooth for tethering a mobile phone to a laptop, then you may follow the steps below:
- The first step is to pair your phone to the laptop. On a PC/laptop, you may go into “Settings”, then “Devices” and then “Bluetooth & other devices”. There you can find the option to add your phone and pair it.
- Once the pairing is done, you may have an additional step in some phones (e.g. some Android phones) to enable Bluetooth tethering by tapping a toggle button as shown in the picture below. In iPhones, you don’t have this step.
- Then you need to go into your PC/laptop “Settings”–>”Network & Internet”, and then “Change adapter options”.
- There you should see “Bluetooth Network Connection”, which you can right click to be able to view “Bluetooth network devices”.
- When you view the Bluetooth network devices, you should see the name of your paired phone on the computer screen.
- Finally, you right-click on the device/phone and connect using “Access Point”.


Conclusion
Tethering and mobile hotspots are interrelated concepts. A mobile hotspot is a type of tethering that enables you to use your mobile phone as a Wi-Fi hotspot so that you can connect any of your internet-capable devices such as laptops, tablets, smart TVs etc., to the internet. However, tethering is not limited to mobile/WiFi hotspots only and can be achieved through Bluetooth and USB cable. Smartphones have the option to enable portable mobile hotspots that utilise the existing data allowance within your mobile tariff to provide WiFi coverage.
While tethering is a good option to connect your devices to the internet using mobile data, there are also some downsides to be aware of. When you use your smartphone as a hotspot, it emits WiFi signals, which can quickly drain your smartphone’s battery. The range of a mobile hotspot created through a smartphone is not great, so if you connect multiple devices to your smartphone hotspot, you can’t take your phone too far away from the devices without interrupting the WiFi signal. If using mobile internet is a more frequent thing for you, getting a dedicated mobile broadband router or MiFi router might be a more practical option. MiFi routers are purpose-built, and some even have Ethernet ports which can come in handy. You will also need an additional mobile connection, i.e. a data-only SIM for your MiFi device.
Here are some helpful downloads
Thank you for reading this post. I hope it helped you in developing a better understanding of cellular networks. Sometimes, we need extra support, especially when preparing for a new job, studying a new topic, or buying a new phone. Whatever you are trying to do, here are some downloads that can help you:
Students & fresh graduates: If you are just starting, the complexity of the cellular industry can be a bit overwhelming. But don’t worry, I have created this FREE ebook so you can familiarise yourself with the basics like 3G, 4G etc. As a next step, check out the latest edition of the same ebook with more details on 4G & 5G networks with diagrams. You can then read Mobile Networks Made Easy, which explains the network nodes, e.g., BTS, MSC, GGSN etc.
Professionals: If you are an experienced professional but new to mobile communications, it may seem hard to compete with someone who has a decade of experience in the cellular industry. But not everyone who works in this industry is always up to date on the bigger picture and the challenges considering how quickly the industry evolves. The bigger picture comes from experience, which is why I’ve carefully put together a few slides to get you started in no time. So if you work in sales, marketing, product, project or any other area of business where you need a high-level view, Introduction to Mobile Communications can give you a quick start. Also, here are some templates to help you prepare your own slides on the product overview and product roadmap.